
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). It aims to shorten the systems development life cycle and provide continuous delivery with high software quality.
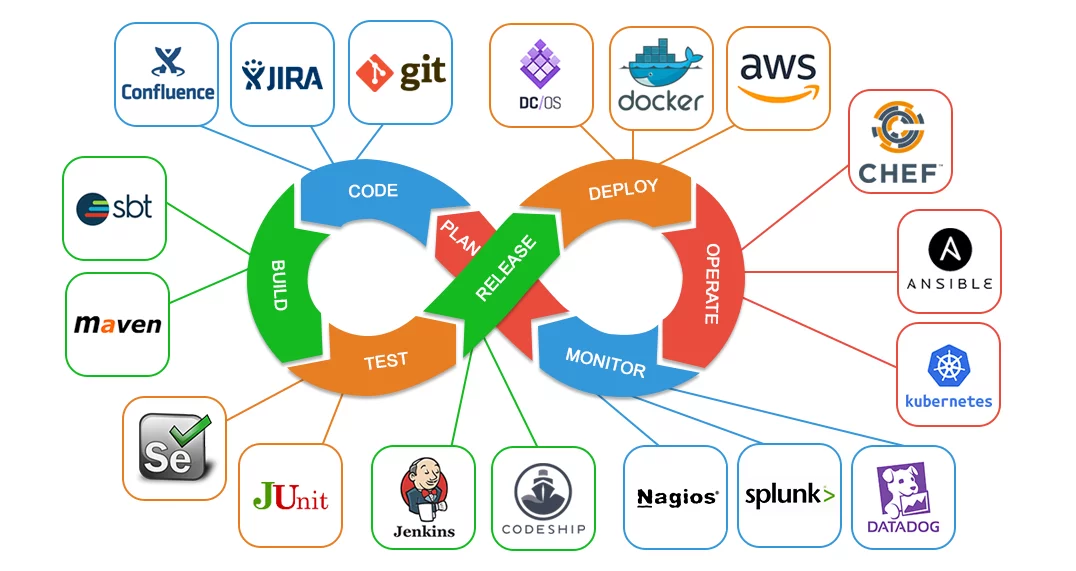
Why this topic?
DevOps has become the predominant approach in the software/product development area. It allows better visibility, coordination and faster iterations in comparison to other relatively older processes like SDLC or Agile, making it popular. Hence, understanding of DevOps processes is a must for a Pentester or DevOps professional.
Pre-requisites?
- Basic knowledge of computers and Software Development process
What will you learn?
This section covers different components/tools used in various phases of the DevOps process. The objective is to teach the user how these components are used in isolation instead of providing the whole pipeline. The labs are focused on learning and not on CTF style evaluation. Each lab comes equipped with a PDF manual that covers the usage of the tools with different easy to follow examples.
References:
- SDLC: https://www.guru99.com/software-development-life-cycle-tutorial.html
- Agile: https://www.atlassian.com/agile
- DevOps: https://aws.amazon.com/devops/what-is-devops/
- SDLC vs Agile vs DevOps: https://victorops.com/blog/agile-vs-devops
Sub-sections/topics to be covered
We are going to cover the following stages of the DevOps process:
1. Version Control System
This phase deals with the writing and management of the source code. The developers write the source code in the selected programming language (using development frameworks) in their favorite IDE (Integrated Development Environment) or text editors. In the case of a small/independent project, the project is processed into a deployable/usable form in IDE itself. However, when multiple developers are working on a big project, the code from all contributors needs to be collected in one place (Code Repository) before the build phase.
2. Building Projects
Building Project labs will cover building/packaging the software/webapp from source code, on a local machine. This section is to give the beginners visibility into what actually happens when the pipeline executes the build step.
3. Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) allows the developer and operations teams to roll out the managed builds and deployments efficiently/automatically. The build process can be triggered automatically or manually whenever the developers have made significant changes to the source code. This reduces the effort on both teams and automation also reduces the error rate.
4. Testing
Functional Testing is done by the developers to make sure that the software/app is working fine. We are focusing on the automated tests written by the developers that can be run automatically after each build.
Deployment Testing covers user interaction automation using the browser and automation tools like Selenium. This testing is done once the web application is deployed on a test server. It ensures that the web application is running correctly in different web browsers and a user can perform different operations successfully on it.
5. Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) covers the tools used to automate the creation of setup for deployment (or test deployment) of the project.
6. Monitoring
Monitoring covers the tools used to monitor the project/application post deployment (or test-deployment). The user interaction, load testing and longevity testing is done in the test deployment and the results/logs are observed by the monitoring framework. Similarly, in case of production deployment, the continuous monitoring ensures that any issues/crashes occurring on the project can be recorded and reported to the developers and operations team, so they can work on fixing it.
